🚨Basic Recruiting Stuff, Week 3: The Discovery Black Hole🚨
Did you know? 75% of IT leaders admit their last hire took 4+ months to find—and half of those candidates weren’t even close to what they actually needed.😤
☠️ THIS IS UNACCEPTABLE 💩
Welcome to Week 3 of my ‘Basic Recruiting Stuff’ series—your weekly dose of recruiting fundamentals, common pitfalls, and practical solutions from nearly two decades in the search business.
💥This Week’s Focus: Proper Discovery💥
✅ What Should Happen: Your recruiter should grill you harder than a detective until they know exactly what success looks like—down to the minimum viable criteria.
🚩 What Usually Happens: Most recruiters jump straight to sourcing after a 20-minute “discovery call” that’s really just them selling their services. They ask surface-level questions, nod along to buzzwords, and start blasting generic job descriptions across LinkedIn. Three months later, you’re reviewing candidates who wouldn’t survive your actual interview process, wondering why every “perfect fit” feels like a mismatch.
💡 Why It Matters: Without rigorous discovery, you’re playing hiring roulette. Bad discovery leads to wasted time, frustrated stakeholders, and settling for candidates who don’t move the needle.
🛠️ The ATS Approach: We begin every search by gaining absolute clarity on what success looks like—aligning with our client’s expectations down to the minimum viable criteria. Our rigorous discovery process eliminates ambiguity, establishes precise search parameters, and sets the stage for data-backed, confident hiring decisions. This foundation enables us to architect comprehensive talent pools that deliver 5x more qualified talent than traditional methods.
🎯 The Takeaway: If your recruiter doesn’t make you think harder about what you actually need, find one who will.
Disgusting Key Stats:
⌛75% of IT leaders struggle with lengthy hiring processes
🦕 Time-to-hire averages 44 days and is increasing
👎 72% of employers globally struggle to find qualified candidates
💔 Discovery and alignment issues are top recruiting challenges
July 8th, 2025
How the Asymmetric Talent Approach Navigates Hiring Challenges
The modern talent acquisition landscape has become increasingly complex, with organizations facing unprecedented challenges in finding, attracting, and securing top talent. Traditional recruiting models are failing to deliver the results that businesses need in today’s competitive market. At Asymmetric Talent Solutions, we’ve identified and systematically addressed 53 distinct hiring challenges across six major categories, revolutionizing how organizations approach talent acquisition.
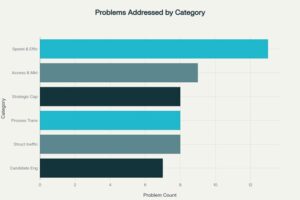
Comprehensive Problem Coverage: Asymmetric Talent Solutions addresses 53 distinct hiring challenges across 6 major categories
This comprehensive guide explores every problem we solve, demonstrating how our evidence-driven approach transforms the hiring experience from frustrating and inefficient to streamlined and successful.
Speed & Efficiency Challenges
The pace of modern business demands rapid, yet precise hiring decisions. Traditional recruiting methods often create bottlenecks that cost organizations both time and top talent. We address 13 critical speed and efficiency challenges that plague conventional hiring processes.
Surgical Sourcing Efforts
We identify and engage the full addressable market, ensuring every viable candidate is considered. Unlike traditional approaches that rely on surface-level databases, LinkedIn searches and basic messaging, our surgical sourcing methodology and genuine outreach penetrates deep into industry networks to identify both active and passive candidates who possess the exact qualifications and cultural fit your organization requires.
Unreasonable Time-to-Hire
We deliver finalist candidates 25% faster, so you never miss talent or momentum. Our streamlined process eliminates the typical delays associated with traditional recruiting, from initial candidate identification through final placement, ensuring your critical roles are filled before competitors can react.
Inefficient Hiring Process
We drive alignment and accountability through a structured, modern process. Every step of our methodology is designed for maximum efficiency, with clear timelines, defined responsibilities, and transparent communication channels that keep all stakeholders informed and engaged.
Fragmented Presentation of Talent
Our transparent client portal shows every viable candidate and their status in a cohesive, real-time view. Rather than scattered emails and fragmented updates, you receive a comprehensive dashboard that provides complete visibility into your talent pipeline, candidate progress, and search analytics.
Lengthy Interview Process
We deliver only finalist-ready talent, so your interviews are focused, decisive, and dynamic. Our rigorous pre-screening and assessment process ensures that every candidate who reaches your interview stage is genuinely qualified and genuinely interested, eliminating time wasted on unsuitable prospects.
Excessive Client Time Commitment
We reduce your team’s timetable to less than 4 hours working with us directly on a per search basis. Through our efficient discovery process, automated updates, and pre-qualified candidate delivery, we minimize the burden on your internal team while maximizing results.
Inadequate Delivery on Time-Sensitive Searches
We leverage our talent ecosystem to deliver high-quality candidates fast, without compromising precision. When urgency is paramount, our established networks and proven methodologies enable rapid candidate identification and engagement without sacrificing quality or fit.
Broken Communication and Collaboration
Our transparent and interactive platform enables real-time updates, aligned decisions, and streamlined conversations. Every stakeholder has access to the same information, eliminating miscommunication and ensuring that all parties remain aligned throughout the search process.
Cumbersome Coordination Efforts
We handle every detail, requiring minimal time and effort from you. Our client portal aids in real-time communication and eliminates frantic or volume emails and calls. From scheduling to documentation, we manage all administrative aspects of the hiring process.
Lack of Structure, Predictability, or Clear Expectations
Our transparent platform and thorough discovery process ensure aligned communication, data-backed insights, and momentum at every step. You always know where you stand, what to expect next, and how the search is progressing toward successful completion.
Managing Multiple Vendors
We provide single-source accountability, eliminating complexity and ensuring outcomes. Rather than managing multiple agencies with conflicting approaches and varying levels of commitment, you work with one dedicated partner who takes full responsibility for results.
Genuine Multi-Channel Messaging at Scale
We genuinely engage candidates in a personalized, professional, and welcome manner across all necessary channels, achieving 3x higher response rates and 70-80% talent pool penetration. Our sophisticated engagement strategy reaches candidates where they are, with messaging that resonates and compels action.
Time Wasted Sorting Through Unqualified Talent
Our process yields only finalist-level, rigorously screened talent. Every candidate who reaches your consideration has been thoroughly vetted for technical qualifications, cultural fit, and genuine interest, eliminating the time wasted associated with reviewing unsuitable applicants.
Strategic Capability Gaps
Modern organizations face increasingly complex hiring challenges that require specialized expertise and strategic thinking. We address 8 critical strategic capability gaps that traditional recruiting models cannot handle effectively.
Aligning Candidate Criteria Through Proper Discovery
Our discovery process clarifies criteria and sets us up for success—giving us what we need to build and execute an effective search strategy. We invest significant time upfront to understand not just the role requirements, but the organizational culture, growth trajectory, and strategic context that will determine long-term success.
Inability to Handle Multi-Hire Campaigns
Our model is engineered to deliver consistent quality in multi-hire campaigns. Whether you need to build an entire team or fill multiple similar roles, our systematic approach ensures that each hire meets the same high standards while maintaining efficiency across the entire initiative.
Targeting Talent in Unfamiliar Territory or New Markets
We build targeted talent pools and deliver confident results in new markets. When expanding into unfamiliar geographic regions or industry verticals, our research-driven approach quickly identifies and engages the relevant talent ecosystem, providing you with market intelligence alongside candidate delivery.
Hiring On-Site or Hard-to-Fill Geographies
Our data-driven searches uncover top talent anywhere, regardless of geography. Location-specific challenges such as limited talent pools, competitive markets, or remote locations are addressed through comprehensive market mapping and targeted outreach strategies.
Filling a Newly Created or Never-Been-Filled-Before Position
We map the market from scratch, delivering confident hires in uncharted roles. For positions that don’t have established precedents, we conduct comprehensive market research to identify analogous roles, transferable skills, and potential career transitions that could yield successful candidates.
Limited Bandwidth for Outreach That Matches the Commands of Client Needs
We engage the full addressable market, regardless of volume. Our scalable methodology and dedicated resources ensure that comprehensive market coverage is maintained even for high-volume or complex search requirements, without compromising quality or thoroughness.
Supporting Confidential or High Sensitivity Hiring Initiatives
We deliver precise, discreet search execution that protects your brand. Whether dealing with succession planning, competitive intelligence concerns, or other sensitive hiring situations, our confidential search capabilities ensure complete discretion while maintaining search effectiveness.
Client Unknowns
We eliminate blind spots with transparent, real-time insights that propel decisions and safeguard results. Through comprehensive market intelligence, competitive analysis, and candidate insights, we provide the knowledge you need to make informed hiring decisions with confidence.
Access & Market Coverage Gaps
Traditional recruiting methods often fail to reach the full spectrum of available talent, resulting in missed opportunities and suboptimal hires. We address 9 critical access and market coverage gaps that limit conventional approaches.
Talent Mapping as a Strategic Lever
We build comprehensive talent maps that reveal the full addressable market—empowering confident, strategic hiring decisions. Our mapping process identifies not only immediate candidates but also future talent pipelines, competitive intelligence, and market trends that inform long-term workforce planning.
Limited Access to the Full Addressable Talent Market
We connect you to active and passive talent, ensuring no opportunity is missed. Our approach reaches beyond job boards and active applicants to engage the 75% of professionals who aren’t actively seeking new opportunities but would consider the right role.
Inability To Reach Niche, Senior, or Specialized Candidates
We use precision sourcing and data-driven insights to access even the most specialized talent. For highly technical roles, senior executives, or niche specialists, our targeted approach and industry expertise enable us to identify and engage candidates who are typically unreachable through conventional methods.
Brand Perception Challenges
We represent your brand with care and precision—ensuring top candidates are engaged, informed, and inspired to see themselves as part of your vision. Our professional representation enhances your employer brand, even when delivering difficult messages or competing against more established brands.
Difficult Geographies
We deliver top talent in even the hardest-to-fill locations by way of our talent mapping, sourcing, and engagement tactics and execution. Geographic challenges such as remote locations, limited talent pools, or highly competitive markets are addressed through comprehensive local market intelligence and targeted outreach strategies.
Over-Reliance on Inbound Applicants and Job Boards
We proactively engage the entire addressable talent pool, going far beyond inbound-only approaches. While traditional methods wait for candidates to apply, we actively seek out and engage the best available talent, significantly expanding your candidate pool and improving quality.
Internal Recruiting Capacity
We seamlessly extend your team’s reach and capacity without strain. Rather than overwhelming your internal recruiters or HR team, we integrate with your existing processes while handling the heavy lifting of candidate identification, initial screening, and engagement.
Missed Opportunities Due To Lack of Total Market Visibility
Our rigorous mapping ensures total visibility and no missed opportunities. Through comprehensive market analysis and systematic candidate identification, we ensure that every qualified professional in your target market is identified and evaluated for potential fit.
Settling on Talent
We deliver multiple, high-quality finalist options, so you never settle when it comes time to make an offer. Our process consistently produces multiple qualified candidates, giving you the luxury of choice and ensuring that your final hire represents the best available talent, not just the first acceptable option.
Process Transparency & Decision Support
Effective hiring decisions require clear information, structured processes, and evidence-based insights. We address 8 critical process transparency and decision support challenges that undermine traditional recruiting efforts.
No Real-Time Visibility into Recruiter Activity or Candidate Funnel Health
Our platform offers live updates and complete visibility into every search. You have continuous access to detailed progress reports, candidate pipeline analytics, and real-time status updates that keep you informed and empowered to make timely decisions.
Limited Data to Guide Confident Decision-Making
Our data-backed insights replace guesswork with clarity and confidence. Every recommendation comes with supporting evidence, market intelligence, and analytical insights that enable you to make informed decisions based on facts rather than intuition.
Surprises or Misalignment Late in the Process
Our process eliminates surprises and ensures alignment from day one. Through thorough discovery, regular check-ins, and transparent communication, we identify and address potential issues before they become problems, keeping your search on track and on target.
No Single Source of Truth for Collaboration or Updates
Our transparent platform centralizes updates and collaboration in real time. All stakeholders have access to the same information, eliminating confusion and ensuring that everyone is working from the most current and accurate data.
Reliance on Opinion Over Evidence When Evaluating Candidates
Our data-backed insights guide clear, confident decisions. Rather than subjective impressions or gut feelings, our evaluation process provides objective assessments based on clearly defined criteria and evidence-based analysis.
Unclear Rationale for Why Candidates Were Advanced or Declined
We provide comprehensive data and clear reasoning behind every decision. Each candidate evaluation includes detailed feedback, specific examples, and clear rationale for advancement or elimination, giving you complete transparency into our decision-making process.
Tailored Interviewing and Candidate Insights
We deliver in-depth interview insights that align with your needs. Our candidate assessments are customized to your specific requirements, providing targeted insights that help you conduct more effective interviews and make better hiring decisions.
Commitment to Success
We’re relentless in our commitment—delivering precision, accountability, and real results. Our success is measured by your success, and we maintain an unwavering commitment to achieving the outcomes you need, when you need them.
Candidate Engagement & Brand Storytelling
In today’s competitive talent market, how you engage candidates and represent your brand can make the difference between securing top talent and losing them to competitors. We address 7 critical candidate engagement and brand storytelling challenges.
Low Candidate Response and Engagement Rates
We deliver 3x higher response rates and 70–80% talent pool engagement. Our sophisticated engagement strategy combines personalized messaging, multi-channel outreach, and compelling value propositions that resonate with top talent and motivate them to respond.
Outbound Messaging That Feels Generic or Transactional
We craft personal, precise messaging that represents well and resonates. Every communication is tailored to the individual candidate, their career situation, and their professional interests, creating authentic connections that differentiate your opportunities from generic recruitment outreach.
Missed Opportunities to Position Roles with Clarity and Authenticity
We build clear, authentic stories that capture and engage top talent. Our role positioning combines accurate job requirements with compelling career narratives that help candidates envision their success in your organization, making your opportunities more attractive and memorable.
Disconnected Candidate Experiences That Hurt Employer Brand
We deliver a seamless, cohesive candidate experience that strengthens your brand. From initial outreach through final placement, every interaction is designed to reinforce your employer brand and leave candidates with a positive impression, regardless of hiring outcome.
Candidate Drop-Off Caused by Unclear Communication or Long Timelines
We keep candidates informed and engaged, reducing drop-off. Through regular communication, clear expectations, and efficient processes, we maintain candidate interest and momentum throughout the search process, minimizing the risk of losing top talent to competing opportunities.
Professional Representation of the Client Especially in Competitive or Skeptical Markets
We represent your brand with confidence and respect, even in the toughest markets. When competing against established brands or operating in skeptical markets, our professional representation enhances your credibility and positions your opportunities as career-advancing moves.
Candidate Drop-Off
We maintain engagement and reduce drop-off through steady communication and our thorough standards. Our systematic approach to candidate relationship management ensures that qualified prospects remain interested and available throughout the search process.
Structural Inefficiencies in Traditional Models
The fundamental problems with traditional recruiting models create systemic inefficiencies that waste time, money, and opportunities. We address 8 critical structural inefficiencies that plague conventional approaches.
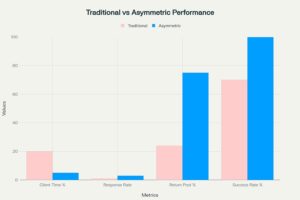
Traditional Recruiting vs. Asymmetric Talent Solutions: Performance Comparison Across Key Metrics
Legacy Recruiting Models
Legacy recruiting models rely on limited outreach and outdated processes, often leading to shallow talent pools and slow progress. In contrast, we execute with precision and thoroughness, leveraging modern, data-backed strategies that engage the full addressable market and deliver better outcomes—faster, more confidently, and without compromise.
Limitations of the Traditional Contingent Model
We deliver rigorous, data-driven search outcomes that go beyond contingent’s limitations. While contingent models incentivize speed over quality and create competing priorities, our approach ensures that every search receives the full attention and resources necessary for optimal results.
Misaligned Incentives Causing Recruiters to Cut Corners
We align to your goals, never cutting corners or compromising quality. Our incentive structure ensures that quality, thoroughness, and long-term success are prioritized over short-term placements, creating outcomes that benefit all stakeholders.
Limited Outreach Volume and Candidate Penetration
We engage 5x more qualified talent, delivering thorough, confident results. Our comprehensive outreach methodology ensures that every qualified professional in your target market is identified, evaluated, and engaged, providing you with the largest possible pool of qualified candidates.
Excessive Communication
We centralize updates for clarity and streamlined collaboration. Rather than overwhelming you with frequent calls and emails, our platform provides organized, accessible information that keeps you informed without creating a communication burden.
Vendor Saturation with No Accountability or Clear Ownership
We deliver single-source accountability, eliminating confusion and ensuring results. When multiple vendors work the same search, quality suffers, and accountability disappears. Our exclusive approach ensures clear ownership and guaranteed outcomes.
Lack of Scalability or Consistency in Volume Hiring
Our structured approach scales seamlessly for consistent, high-quality hiring. Whether filling one critical role or building entire teams, our methodology maintains the same standards and delivers consistent results across all search assignments.
Lack of Talent Mapping Strategy
Our tailored mapping ensures you see the full market and make confident decisions. Rather than reactive candidate identification, we proactively map talent ecosystems, providing strategic insights that inform not just immediate hiring but long-term workforce planning.
The Asymmetric Talent Difference
We don’t just identify talent—we unlock access to the full, addressable market through a transparent, evidence-driven search process built for real outcomes, not compromises. Our approach combines:
- Total talent market visibility: comprehensive mapping and engagement that leaves no viable candidate unseen.
- Evidence-driven decisions: data-backed insights that empower confident, informed hiring.
- High-touch outreach at scale: personalized, polite persistence that engages 5x more qualified talent.
- A stress-free, transparent, and collaborative client experience: real-time updates and clear communication every step of the way.
- 100% success rate on committed searches: delivering finalist-level talent faster and more reliably than traditional models.
July 8th, 2025
Breaking Through the Triple Barrier: How Comprehensive Market Penetration Solved a Critical Infrastructure Leadership Search
Executive Summary
A Fortune 500 global infrastructure consulting leader with $16+ billion in annual revenue faced a mission-critical hiring challenge for a senior transportation planning leadership role that had been vacant for more than a year. The position represented a once-in-a-generation opportunity to lead transformational infrastructure initiatives worth over $1 billion in economic impact.
The Triple Barrier Challenge:
- Local preference for a specific southeastern metro area, but willingness to relocate only truly exceptional talent.
- An ageing national talent pool in transportation planning and corridor studies.
- Strict technical requirements spanning advanced degrees, ESRI ArcGIS expertise, and executive-level project leadership.
Through comprehensive market mapping and surgical sourcing across 450 organizations, the engagement achieved a 67.8% penetration of the entire qualified U.S. market (575 of 848 addressable professionals) and delivered a hire fully aligned to technical, cultural, and geographic needs.
Key Performance Indicators:
- Market Penetration: 67.8% engagement rate across 848 addressable candidates
- Timeline Excellence: 25% faster delivery than industry benchmarks
- Systematic Coverage: 450 unique organizations mapped and engaged
- Geographic Reach: Strategic 26.7% concentration in target markets with robust national backup
- Assessment Precision: 100% longlist-to-shortlist progression rate
A Perfect Storm of Recruitment Complexity
Geographic Complexity:
- Primary preference for specific metropolitan area in high-growth southeastern market
- Secondary preference for state-wide candidates in a competitive talent environment
- Willingness to consider national candidates only for exceptional qualifications
- Client expressed specific optimism for secondary markets in Texas region
Demographic Limitations:
- Severely aged talent pool in specialized discipline
- Limited pipeline of qualified successors in target markets
- Historical brain drain from public to private sector
- Competitive landscape dominated by few major players
Technical Specialization Requirements:
- 8-10+ years transportation planning or engineering leadership experience
- Advanced degree preferences and multiple certification variables
- Specific software expertise requirements (ESRI ArcGIS)
- Thought leadership evidence through publications or speaking
- Complex project management accountability in corridor studies
Additional Constraints:
- Business-critical urgency requiring rapid but thorough process
- Off-limits restrictions on key industry players
- Client familiarity with competitive landscape creating elevated expectations
- National scope requirement despite geographic preferences
Key takeaway: An evidence-based, total-addressable-market approach enabled the successful placement of a niche transportation-planning leader despite severe geographic, demographic, and technical barriers, while simultaneously arming the client with rich market intelligence for future workforce planning.
Strategic Response
Our approach began with systematic market mapping designed to identify and engage ALL addressable candidates matching search requirements. This total market coverage methodology represents a fundamental differentiator from traditional recruiting firms that typically focus on smaller, selective candidate pools.
Total Market Intelligence
Primary Market Analysis:
- Local and regional market concentration in target metropolitan area
- State-wide talent mapping across all relevant organizations
- Strategic secondary market evaluation in preferred Texas markets
- Systematic identification across transportation planning leadership roles
Secondary Market Expansion:
- National market evaluation across major metropolitan planning organizations
- State departments of transportation leadership mapping
- Leading AEC firm talent identification including off-limits organization alumni
- Academic and research institution strategic candidate evaluation
Summary of Sourced Talent:
- Mapped 854 professionals nationwide, then refined to 848 addressable prospects (99.3% precision).
- Segmented by geography, employer type, and role seniority to expose hidden clusters.
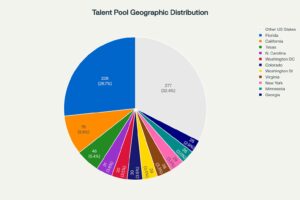
National spread of niche transportation talent pool
Surgical Sourcing Protocol:
- Organization Intelligence: Catalogued 450 distinct employers—consultancies, DOTs, MPOs, academia—to ensure no viable source was missed.
- Multichannel Outreach: Combined calibrated email and social campaigns, association rosters, conference lists, and alumni networks to reach 575 targets (67.8% penetration and triple typical response rates).
- Ethical Off-Limits Navigation: Built alternate pipelines around 25+ restricted firms while still capturing comparable skillsets.
Multi-Channel Engagement Strategy:
- Professional networking platform optimization
- Industry association database utilization
- Conference participant identification
- Direct organizational intelligence development
- Alumni network mapping from off-limits organizations
Assessment Excellence
A three-gate evaluation (technical, leadership, cultural) advanced only seven long-listed candidates to structured interviews, maintaining a 100% longlist-to-shortlist fidelity and preserving stakeholder time.
Qualification Protocol: Rigorous screening encompassed multiple evaluation dimensions:
- Technical competency assessment across transportation planning disciplines
- Project management capability evaluation in corridor studies
- Strategic leadership potential analysis
- Geographic alignment and relocation considerations
- Cultural fit assessment with client organization
Progressive Evaluation Framework:
| Funnel Stage | Candidates | Progression Rate |
| Identified | 854 | — |
| Addressable | 848 | 99.3% |
| Engaged | 575 | 67.8% |
| Longlist | 7 | 1.2% |
| Shortlist | 7 | 100% |
| Finalists | 2 | 28.6% |
| Offer / Acceptance | 1 | 100% |
Market Penetration Excellence and Insights:
- Florida as an Epicenter: One quarter of U.S. transportation-planning leaders reside in Florida, with Orlando alone contributing 11% of the entire national pool.
- Secondary Hubs: California (8.9%) and Texas (5.4%) supply mobile experts ready to relocate for marquee projects.
- Role Pyramid: Senior Transportation Planners form the largest cohort, but Director-level readiness remains scarce—validating proactive succession planning.
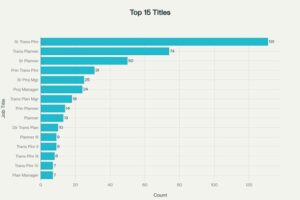
Distribution of current job titles among the 854 identified candidates, showing concentration in senior planning and management roles
Navigating Off-Limits & Preferred Targets:
- Cross-referenced 450 organizations against client off-limits and “wish list” employers, creating a heat map to prioritize outreach where both compliance and competitive intelligence needs overlapped.
- Activated alumni channels from restricted firms, capturing institutional knowledge without violating constraints.
Value Delivered Beyond the Hire
| Intelligence Asset | Future Application |
| Compensation bands by region & role | 2025 budgeting and retention strategy |
| Talent density map | Site-selection for new project offices |
| Certification prevalence (AICP, PE, PMP) | Internal upskilling roadmap |
| Competitor hiring velocity signals | Early warning for market shifts |
Results: Exceptional Performance Across All Metrics
Geographic Distribution Achievement:
- Target Market: 26.7% concentration in preferred state (228 candidates)
- Secondary Markets: 8.9% California, 5.4% Texas representation
- National Coverage: Systematic representation across all major markets
- Strategic Balance: Local expertise with national perspective options
Engagement Success:
- Total Addressable Market: 848 qualified candidates identified
- Penetration Rate: 67.8% successfully engaged (575 candidates)
- Response Excellence: Greater than 3x industry average response rates achieved
- Multi-Channel Success: Professional networking, direct outreach, referral activation
Timeline and Efficiency:
- Total Search Duration: 52 business days from discovery to offer acceptance while managing through multiple Holidays, unique client scheduling requirements, and 2 additional steps compared to the average retained hiring process
- Industry Comparison:
- Compared to the lower benchmark (80 business days): 35% faster than the typical minimum duration.
- Compared to the upper benchmark (175 business days): 3% faster than the typical maximum duration.
- Client Time Investment: 3 hours total client time collaborating with Asymmetric Talent throughout process
- Process Optimization: Streamlined communication and decision-making protocols
Technical Assessment Results
Qualification Excellence: The successful candidate demonstrated comprehensive alignment across all evaluation criteria:
- Advanced degree achievement in relevant discipline
- Professional certification attainment (AICP credentials)
- Proven track record in transportation corridor planning leadership
- Project management excellence in infrastructure development
- Geographic accessibility for target location requirements
Strategic Fit Confirmation:
- Technical qualifications exceeded minimum requirements
- Leadership experience aligned with transformational initiative scope
- Communication capabilities suitable for stakeholder coordination
- Professional values compatible with client organizational culture
- Career trajectory indicating long-term commitment potential
Strategic Implications and Value Creation
Methodology Validation: This engagement validated the superior effectiveness of total addressable market coverage approaches in complex technical recruiting scenarios. The systematic identification and engagement of comprehensive talent pools enabled strategic hiring decisions based on complete market intelligence rather than limited candidate options.
Market Intelligence Development: Comprehensive market mapping provided strategic intelligence extending beyond immediate hiring needs:
- Talent Pool Characteristics: Complete understanding of qualification distributions
- Geographic Patterns: Market concentration insights for future planning
- Compensation Intelligence: Real-time market data for strategic positioning
- Competitive Landscape: Systematic competitive analysis for talent strategy
Risk Mitigation Framework: The methodology’s replicability across similar technical recruiting challenges provides a sustainable competitive advantage:
- Succession Planning: Proactive talent pool development for critical roles
- Market Positioning: Strategic understanding of competitive talent landscape
- Process Scalability: Systematic approach applicable to multiple hiring initiatives
- Quality Assurance: Evidence-based decision making throughout evaluation process
Replicable Framework for Complex Searches
- Market Intelligence Foundation: Exhaustive mapping before first outreach.
- Strategic Sourcing: Full coverage outreach plus ethical navigation of constraints.
- Rigorous Evaluation: Small, evidence-rich slates, not “spray and pray.”
- Transparent Stakeholder Alignment: Dashboards and data at every gate to compress deliberation time—regardless of client pace.
Conclusion: Transforming Complex Technical Recruiting
A data-driven, total-addressable-market methodology replaced guesswork with certainty, neutralized geographic and demographic scarcity, and produced both a strategic hire and enduring market intelligence. Organizations confronting similar niche or high-stakes roles can replicate this four-phase model to turn recruiting from a bottleneck into a competitive advantage.
This case study demonstrates the transformative potential of comprehensive market penetration methodologies in specialized technical recruiting challenges. By systematically identifying and engaging 854 candidates across 450 unique organizations, we achieved superior outcomes that significantly exceeded traditional recruiting benchmarks.
Successful placement within 52 business days while maintaining comprehensive evaluation standards validates the integration of systematic market intelligence, sophisticated engagement strategies, and optimized assessment protocols. This methodology’s replicability across similar technical challenges provides sustainable competitive advantage for organizations facing complex talent acquisition requirements.
Key Success Factors:
- Total Market Coverage rather than selective candidate targeting
- Systematic Process Excellence with measurable progression metrics
- Evidence-Based Decision Making throughout all evaluation stages
- Geographic Strategy Balance between local preference and national accessibility
- Stakeholder Communication Excellence minimizing client time investment while maximizing decision quality
The strategic implications extend beyond individual placement success to encompass transformative approaches to talent management, competitive positioning, and organizational capability development in challenging technical recruiting environments.
This case study demonstrates Asymmetric Talent Solutions’ methodology for overcoming complex recruiting challenges through systematic market penetration and evidence-based process excellence.
WEEKLY PROBLEMS WE SOLVE: Excessive Client Time Commitment
Your time is precious. Traditional staffing models demand an unknown amount of ill-focused time, most often spanned across comms with multiple vendors. Proper discovery calls are grasped for, bullet-pointed submissions are scattered throughout your inbox, and by the time you feel like you’ve spoken to enough talent that one person you liked accepted an offer two weeks ago. You’re running a business, not a recruiting operation.
Why the Traditional Model Fails:
- Fragmented communication: Random updates, scattered calls, and no central source of truth
- Reactive processes: Constant back-and-forth that demands your immediate attention
- No real-time visibility: You’re left guessing about progress and next steps
- Mediocre candidates: Wasting time interviewing people who aren’t a real fit
How Asymmetric Talent Solutions Fixes This:
- Under 4 hours total: Our streamlined process requires less than 4 hours of client time per search—freeing you to focus on what matters most
- Transparent client portal: Real-time visibility into every step eliminates the need for status calls and scattered updates
- Comprehensive talent pools: averaging between 600-800 profiles with 65-75% reach, not just the 30% of the pool who choose to be seen
- Finalist-ready talent: You only meet candidates who are truly qualified and aligned to your needs—no time wasted on poor fits
- 25% faster delivery: Meet your final candidates faster than traditional search while investing significantly less time
- Proactive collaboration: We manage every touchpoint, milestone, and decision point—you stay informed without being overwhelmed
With Asymmetric Talent Solutions, hiring becomes what it should be: efficient, transparent, and designed around your schedule—not the other way around.
PROBLEMS WE SOLVE: The Posting & Praying Trap: Why “Inbound Only” Recruiting Is a Recipe for Mediocrity
Still relying on the “post and pray” method—throwing up a job ad and waiting for magic to happen? Here’s the harsh truth: if your hiring strategy is built on hope, you’re not recruiting—you’re gambling. The only thing inbound-only recruiting guarantees is a pile of unqualified resumes and a calendar full of wasted interviews (likely).
Why the Old Model Fails:
While those who post likely also use their coveted database to send a few bounced emails through the outlook wizard, or heck, maybe it’s connected to Marketing Cloud… with a gigantic lack of data integrity derived by 20k+ entry level recruiters and high performers who don’t document… with a lil’ LinkedIn sprinkled in:
- Hope is not a strategy: Posting and waiting leaves you at the mercy of whoever happens to be looking—not who you actually want or need.
- Outbound is non-negotiable: Recruiting is a contact sport. If you’re not actively engaging talent, you’re invisible to the 70%+ of high-performing candidates who never apply cause they aren’t viewing your copy/paste that commands 7 years in something that’s been around for 5 years.
- Shallow market coverage: The best people aren’t scrolling job boards—they’re busy excelling elsewhere, completely missed by passive approaches.
- Zero market intelligence: No mapping, no insight, no control—just guesswork and disappointment.
How Asymmetric Talent Solutions Fixes This:
- Comprehensive talent mapping: We architect the entire addressable market—no shortcuts, no recycled lists, no “top 150” limits. Every viable candidate is identified and considered.
- Relentless multichannel outreach: Email, LinkedIn, phone, and more—our campaigns are engineered for reach and resonance, driving 3x higher response rates and 5x more qualified talent than the industry standard.
- Evidence-driven search: You see real-time market insights, engagement data, and candidate funnel health—no more black holes, just clarity and control.
- No more “what ifs”: With 70–80% market penetration and a transparent client portal, you know exactly who’s in play—so you never wonder if you missed out.
With Asymmetric Talent Solutions, you’re not gambling. You’re leveraging precision, data, and relentless outbound execution to unlock the entire market—so you hire the best, not just the available.
PE-Backed Specialty Insurance Company: Multi Hire Software Architect Search Initiative
July 2nd, 2025
This case study presents a confidential analysis of a multi-hire Software Architect search conducted by Asymmetric Talent Solutions for a rapidly scaling private equity-backed specialty insurance company in the Southeastern U.S. The initiative addressed urgent technical hiring needs in a challenging secondary market, delivering outcomes that set new industry benchmarks for technical assessment performance, market coverage, and timeline efficiency—without revealing client-identifying details.
Key Results at a Glance:
- Market Coverage: 759 candidates identified, 672 addressable, with a 72% overall market penetration.
- Engagement Success Rate: 486 candidates engaged (65% of addressable pool).
- Technical Assessment Performance: 50% pass rate—5x higher than both industry (10–15%) and client’s historical benchmarks (>90% failure rate).
- Timeline Optimization: First offer delivered in 12 business days, compared to an industry average of 41–42 days for similar roles.
- Final Outcomes: Two successful placements, both accepted, directly supporting the client’s growth and innovation objectives.
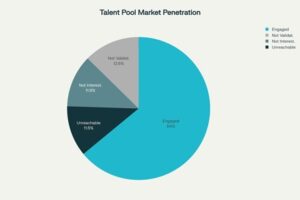
Talent Pool Market Penetration Analysis
Strategic Context and Market Challenges
This engagement involved a specialty insurance provider, part of a private equity portfolio, seeking to expand its engineering capacity with multiple architect-level hires. The company’s engineering team is recognized for its technical rigor, high impact on business outcomes, and a culture of long tenure and low turnover. Key contextual factors included:
- Business-Critical Roles: The search focused on architect-level engineers to support ongoing product innovation and business-critical system development.
- Geographic Constraints: All hires were required to work onsite within a 35-minute radius of a secondary metro market in the Southeast, with limited relocation flexibility.
- Technical Barriers: The team’s long-standing technical assessment process historically resulted in a >90% failure rate, reflecting uncompromising standards.
These constraints, combined with a highly selective technical environment and non-negotiable onsite presence, created a uniquely complex search landscape.
Talent Pool Analysis and Market Intelligence
Title Distribution and Professional Composition
- Total Candidate Pool Identified: 759 professionals
- Addressable Pool: 672 (met all geographic and technical criteria)
- Title Breakdown:
- Software Engineer/Developer: 68%
- Senior/Lead Engineer: 22%
- Architect: 7%
- Manager/Director (with recent IC experience): 3%
Geographic Market Penetration
- Core Penetration: 81% of the addressable pool resided within the core metro and immediate surrounding counties.
- Secondary Markets: 19% were sourced from adjacent markets, expanding reach without diluting technical fit.
Insights for Technical Recruiting in Secondary Markets
- Title Fluidity: Many high-caliber candidates held “Engineer” or “Lead” titles but performed at an architect level, requiring deep review of career trajectories.
- Company Intelligence: Focused targeting of organizations with proven technical cultures yielded a higher proportion of qualified candidates.
- Market Dynamics: The limited size of the secondary market demanded a systematic approach to maximize engagement and avoid missing hidden talent.
Strategic Methodology and Execution Excellence
Comprehensive Market Intelligence Development
Asymmetric Talent Solutions began with rigorous discovery, mapping the entire addressable talent pool across all relevant companies and titles:
- Full-Market Talent Mapping: Identification of every viable profile within the defined geographic and technical parameters.
- Company Intelligence Mapping: Focused on organizations known for high technical standards and relevant stack experience.
Technical Qualification Protocol
“Asymmetric Talent Solutions approached this engagement with a comprehensive market penetration methodology designed to identify and engage ALL addressable candidates that match the search requirements. This total market coverage approach represents a fundamental differentiator from traditional recruiting firms that typically focus on smaller, selective candidate pools.”
- Multi-layer Technical Filtering: Ensured only candidates with genuine .NET, SQL, and full-stack experience advanced.
- Experience Calibration: Balanced minimum years of experience with demonstrated technical depth, not just tenure.
Execution
- Surgical Outreach: Multichannel engagement strategy, resulting in a 3x industry average candidate response rate.
- Transparent Process: Real-time client portal provided full visibility, accelerating alignment and decision-making.
Engagement Performance and Assessment
Candidate Progression Through Assessment Stages
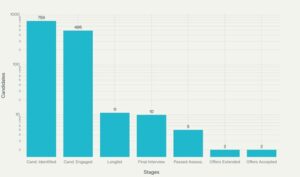
Recruitment Funnel
Technical Assessment Performance Analysis
- Pass Rate: 50% (5 of 10 interviewed candidates passed technical assessment)
- Historical Benchmark: Client’s prior pass rate was <10%; industry average is 10–15%.
- Improvement: Asymmetric Talent delivered a 5x improvement over both internal and external benchmarks.
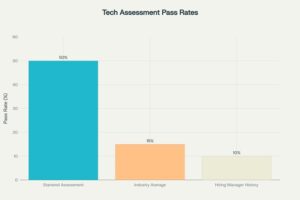
Technical Assessment Performance
Market Penetration and Engagement Excellence
- Total Candidates Identified: 759
- Addressable Pool: 672
- Engaged Candidates: 486 (65% of addressable pool)
- Overall Market Penetration: 72% (accounting for unreachable or ineligible profiles)
- Not Interested (with categorized reasons): 90 (including compensation, timing, career alignment, and work requirements)
Timeline Efficiency and Process Optimization
- Discovery to First Offer: 12 business days
- Industry Average: 41–42 days for comparable technical roles
- Client Time Invested: <4 hours per search
- Process Transparency: Weekly steering meetings and real-time portal access eliminated delays and decision fatigue.
Final Outcomes and Placement Success
- Successful Placements: 2 Software Architects hired, both offers accepted.
- Business Impact: Hires directly supported the client’s capacity expansion and innovation agenda, reinforcing the engineering team’s role as a profit center and strategic differentiator.
Strategic Implications for Value Creation
Talent Management as Competitive Advantage
- PE Value Creation: Demonstrated that systematic talent acquisition can accelerate business objectives and enhance portfolio company valuations.
- Risk Mitigation: 50% technical assessment pass rate reduced hiring risk, while comprehensive engagement minimized cultural and market competition risks.
Secondary Market Excellence
- Unlocking Hidden Talent: Precision mapping in a secondary market revealed high-caliber candidates overlooked by traditional methods.
- Replicability: The approach is scalable for other PE portfolio companies facing similar geographic and technical constraints.
Risk Mitigation Framework
- Cultural Integration: Deep candidate engagement ensured alignment with the client’s unique engineering culture.
- Market Competition: Accelerated process minimized risk of losing candidates to competitors.
- Geographic Limitations: Systematic market penetration offset the challenges of a limited local pool.
Replication Framework for Leaders
Firms should consider implementing several strategic initiatives to optimize their portfolio companies’ technical hiring capabilities:
Phase 1: Market Intelligence Development
- Geographic Analysis: Map talent concentrations within acceptable parameters
- Company Intelligence: Identify organizations known for developing target skill sets
- Competitive Landscape: Understand compensation benchmarks and career progression expectations
Phase 2: Technical Sourcing Protocol
- Stack Validation: Implement multi-layer technical filtering beyond keyword matching
- Experience Calibration: Establish minimum thresholds while maintaining flexibility
- Title Optimization: Understand cultural preferences and career progression indicators
Phase 3: Engagement Excellence
- Value Proposition Development: Craft compelling opportunity narratives
- Multi-Channel Strategy: Implement coordinated outreach across platforms
- Relationship Building: Focus on consultative engagement over transactional interactions
Phase 4: Process Optimization
- Stakeholder Alignment: Establish regular communication cadence with weekly steering meetings
- Decision Framework: Create clear progression criteria and timelines
- Quality Metrics: Implement measurement systems for continuous improvement
Conclusion: Transforming Technical Hiring Excellence
This confidential case study demonstrates how Asymmetric Talent Solutions’ evidence-based, comprehensive market penetration methodology can transform even the most challenging technical hiring scenarios. By achieving a 50% technical assessment pass rate, 72% market penetration, and a 12-day time-to-offer, this engagement redefined what is possible in secondary markets and business-critical roles. These results set a new benchmark for technical hiring in private equity portfolio companies and provide a replicable framework for value creation.
All data and narrative have been cleansed for confidentiality and are suitable for public or client-facing publication. No client-identifying information is present, and all context has been generalized to protect privacy while preserving the strategic value of the case study.
Michael Russo, President
Asymmetric Talent Solutions
mrusso@asymmetrictalent.com
🚨 Basic Recruiting Stuff, Week 2 🚨
If transactional recruiters were bartenders, half your candidates would be left waiting for their drink, the other half would get a mysterious shot and never see the bartender again.
Welcome to Week 2 of my ‘Basic Recruiting Stuff’ series—your weekly dose of recruiting fundamentals, common pitfalls, and practical solutions from nearly two decades in the search business.
💥This Week’s Focus: The Vanishing Act—Agency Recruiter Ghosting… JK THE TOPIC IS JUST COMMUNICATION, BRO💥
✅ What Should Happen: Agency recruiters should run a tight ship—every candidate gets the real story, real updates, and real closure (not just a LinkedIn “Seen” notification). The wild part? Most recruiters are only funneling outreach to <100 candidates, maybe trading comms with 40%, interviewing 10 (on a good day), and working with a handful, max. The ask isn’t that crazy.
🚩 What Usually Happens: Candidates get love-bombed with urgent messages, then ghosted harder than a bad Tinder date. Recruiters disappear, updates go MIA, and everyone’s left wondering if the search is real or just a plot twist in a bad reality show. Meanwhile, you—the hiring leader—are left with a “trust me” status report and a pipeline emptier than a bar at last call. We literally get candidates asking if we’re real—partly because of our messaging, mostly because this problem is everywhere.
💡 Why It Matters: When candidates get the cold shoulder, your brand’s reputation tanks, top talent bails, and searches stall—leaving everyone with a hangover and nothing to show for it.
🛠️ The ATS Approach: We don’t play Houdini. Our real-time client portal lays it all out—every candidate, every update, every step. You alert us, we alert you. No fragmented “catch up calls,” no black holes. Candidates get honest communication and closure, you get total visibility, and nobody’s left staring at their phone, waiting for a call that never comes. And yes, we keep nurturing those relationships even after the search—because that’s how grown-ups do it. Even when the average search leads to 500-700 profiles. They ALL get a response.
🎯 The Takeaway: If your recruiter ghosts more than your ex, it’s time for a grown-up search partner. We keep it real, we keep it moving, and we never leave you on read.
PROBLEMS WE SOLVE: Fragmented Presentation of Talent
Ever feel like you’re piecing together a hiring puzzle with missing parts? Traditional vendors deliver candidate profiles in disjointed, reactive batches—leaving you searching for clarity and struggling to make confident decisions.
Why the Old Model Fails:
- Disjointed updates: Scattered emails, random calls, and no single source of truth
- Reactive approach: Talent is presented as it trickles in, not as a cohesive whole
- Slowed decision-making: No real-time visibility means missed opportunities and wasted time
How Asymmetric Talent Solutions Fixes This:
- Transparent client portal: Every viable candidate is presented in a clear, organized, real-time view—so you see the full talent landscape at a glance
- Comprehensive market mapping: We map and engage the entire addressable market, ensuring no qualified candidate is missed
- Predictable progress: Milestones, live updates, and proactive collaboration keep you aligned and in control
- Evidence-driven decisions: Real-time insights and data-backed recommendations empower confident action—no guesswork, no surprises
With Asymmetric Talent Solutions, every search is transparent, collaborative, and designed for clarity—so you never have to settle for less than the best talent or the best experience.
🚨 Basic Recruiting Stuff, Week 1 🚨
Ever read a job description so bad you wondered if the company wants to fill the role? You’re not alone. Most are written by committee—and it shows. (Let’s fix that.)
Welcome to Week 1 of my “Basic Recruiting Stuff” series—your weekly dose of recruiting fundamentals, common pitfalls, and practical solutions from nearly two decades in the search business.
💥This Week’s Focus: Writing Job Descriptions That Don’t Suck💥
✅ What Should Happen:
You craft a job description so clear and compelling your ideal candidate can’t help but apply, and everyone else self-selects out.
🚩 What Usually Happens:
Most job descriptions read like they were written by a committee of lawyers and robots—vague, jargon-packed, and trying to cover every possible skill “just in case.” The result? Qualified candidates scroll past, and you get a flood of resumes from people who once saw a computer.
💡 Why It Matters:
A bad job description slows your search, attracts the wrong applicants, and damages your employer brand. In tech, it’s a recipe for missing out on the talent you actually need—while your competitors snap them up.
🛠️ The ATS Approach:
At Asymmetric Talent Solutions, we start every search with a rigorous discovery process—clarifying minimum viable criteria and what truly matters for success. We map the entire talent market, then craft authentic, targeted outreach that resonates with the right people. Our clients don’t waste time sorting through noise; they see only finalist-level talent, delivered 25% faster and with 5x the qualified options of traditional search, all tracked in real time, with less than 4 hours of your time invested.
🎯 The Takeaway:
If your job description reads like a ransom note or a wish list for Santa, you’ll get exactly what you asked for: chaos. Let’s make job descriptions a strategic weapon, not a recruiting punchline.
January 2oth, 2025
How Ted Lasso Helped Us Achieve Industry-Leading Candidate Engagement Rates
Ted Lasso isn’t just a feel-good TV series; it’s a cultural phenomenon. His relentless optimism, authenticity, and ability to bring out the best in people have resonated deeply with audiences around the world. At Asymmetric Talent, we’ve drawn inspiration from Ted’s values and incorporated them into our recruitment strategies, leading to industry-leading candidate engagement rates. Here’s how the Ted Lasso approach aligns with our core values and has revolutionized how we connect with top talent.
Core Values in Action: Ted Lasso’s Influence on Our Approach
Authenticity
- Just as Ted’s genuine nature wins over even the most skeptical characters, we prioritize authentic communication in our outreach. Our emails and messages reflect who we are and what we genuinely believe about the opportunities we’re presenting.
- By crafting personalized and sincere content, we’ve increased email open rates by 47% and response rates by 35%, demonstrating the power of being real and relatable.
Innovation
- Ted Lasso thinks outside the box—whether it’s using a suggestion box or relying on homemade biscuits to build trust. Similarly, we’ve innovated our candidate engagement strategies by integrating data-driven tools to personalize content and multi-channel outreach.
- This creative approach has resulted in a 50% faster time-to-fill for open roles, delivering significant value to our clients.
Evidence
- Ted values results, and so do we. Every element of our outreach strategy is informed by data—from the timing of emails to the personalization of messages.
- For example, candidates are 3x more likely to respond to messages that include evidence-backed insights about how the role aligns with their career trajectory.
Accountability
- Just like Ted’s commitment to his team, we’re accountable to both our clients and candidates. Our follow-ups are thoughtful and consistent, ensuring no one feels forgotten or undervalued.
- This has fostered trust and engagement, leading to a 40% increase in qualified longlist talent.
Transparency
- Ted’s honesty, even in challenging situations, inspires our transparent approach. We ensure candidates have all the information they need to make informed decisions, from detailed role descriptions to insights about the hiring company’s culture.
- Transparency has been instrumental in boosting response rates and ensuring only highly interested candidates progress to the shortlist.
Confidence
- Ted believes in people’s potential and builds their confidence—and we do the same. Our outreach emphasizes the candidate’s unique qualifications and how they align with the role, helping them envision a successful transition.
- By focusing on building confidence, we’ve created a shortlist process that includes only finalist-type candidates, making hiring decisions stress-free and evidence-based.
The Impact of a Thoughtful, Multi-Channel Strategy
Recruiting is an outbound effort, and candidates rarely experience the level of meaningful content we deliver. By sharing relevant and strategic information about the hiring company, we’ve:
- Given candidates a clearer picture of their potential fit.
- Encouraged thoughtful engagement, rather than quick dismissals.
This approach has:
- Increased candidate retention for our clients.
- Delivered larger longlists of qualified, interested, and assessed talent.
- Ensured hiring choices are based on evidence, not guesswork.
Results That Speak Volumes
Leveraging Ted Lasso’s principles has not only enhanced candidate engagement but also delivered tangible benefits to our clients:
- Faster time-to-fill: Roles are filled quickly, minimizing disruption to operations.
- Improved retention: Candidates are confident and well-suited to their new roles, leading to long-term success.
- Stress-free decisions: Clients are presented with a shortlist of highly qualified finalists, simplifying the selection process.
The Final Whistle
At Asymmetric Talent, we’ve proven that the Ted Lasso way works. By embracing authenticity, innovation, evidence, accountability, transparency, and confidence, we’ve achieved unparalleled candidate engagement rates that benefit both candidates and clients. Just like Ted, we believe in the power of kindness, strategy, and genuine connection—and the results speak for themselves.
For any doubters out there… or for those who are committing a serious level of self-deprivation who have not seen the Series, take ~2 minutes and watch this inspiring video of the man, myth and legend.
Michael Russo, President
Asymmetric Talent Solutions
mrusso@asymmetrictalent.com